PUBLISHED: January 10, 2026 | SOURCE: EODB News

The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has released draft guidelines for implementing a Battery Pack Aadhaar System, marking a major step towards improving safety, traceability and lifecycle accountability of electric vehicle (EV) batteries in India. The proposed framework covers EV batteries used in L, M and N category vehicles, as well as industrial batteries above 2 kWh, and introduces a unique 21-character Battery Pack Aadhaar Number (BPAN) to enable structured identification and monitoring across the battery lifecycle.
The draft guidelines closely reflect early safety, traceability and digital monitoring concepts advocated by the National Highways for Electric Vehicles (NHEV) and the Charge Point Operators’ (CPO) Society since 2022. These included recommendations for real-time battery identification, transparent access to battery data, black-box style diagnostics for failures and fire incidents, and end-to-end digital traceability covering ownership, usage and recycling—aimed at strengthening consumer safety, regulatory oversight and confidence in the EV ecosystem.
Welcoming the move, Shri Abhijeet Sinha, Project Director – National Highways for Electric Vehicles, said, “It is encouraging to see policy converging on evidence-based recommendations needed to upgrade technology and modernize India’s EV battery ecosystem. The NHEV pilot’s recommendations from 2022 are becoming guidelines in 2026, which may seem slightly delayed, but this structured battery identity and monitoring framework is now among the most advanced global protocols. It strengthens safety, transparency, and trust in EV batteries. NHEV is working closely with the government, industry, and regulators to deliver a Connected Commercial Vehicle (CCV) Protocol with V2V communication that supports both charging and swapping alternatives for third-generation EVs in India.”
Over the past few years, NHEV and the CPO Society have engaged extensively with policymakers, industry stakeholders and technical experts to advance complementary initiatives such as charging infrastructure deployment, battery swapping frameworks, financing models and standardisation efforts. These initiatives consistently underscored the need for a robust digital backbone for EV batteries—covering specifications, material composition, carbon footprint, State of Health (SoH), lifecycle events and end-of-life outcomes.
NHEV views the draft Battery Pack Aadhaar guidelines as a constructive and timely step towards building a safer, data-driven and globally aligned electric mobility ecosystem in India, and looks forward to contributing further to their refinement and implementation.
— ENDS —
अब EV बैटरियों का भी बनेगा आधार! BPAN से लगेगी फर्जीवाड़े पर लगाम, जानें नया सिस्टम
PUBLISHED: January 05, 2026 | SOURCE: Aaj Tak Digital
Electric Car Battery Aadhaar: बैटरी पैक आधार नंबर (BPAN) एक खास 21 अंकों का अल्फान्यूमेरिक आइडेंटिफिकेशन (पहचान) नंबर होगा, जो हर इलेक्ट्रिक व्हीकल की बैटरी को दिया जाएगा. यह नंबर QR कोड के रूप में भी मौजूद रहेगा.
EV Battery Pack Aadhaar Number: भारत में इलेक्ट्रिक वाहनों के तेजी से बढ़ते चलन के बीच अब उनकी बैटरियों को लेकर भी सरकार एक बड़ा और अहम कदम उठाने जा रही है. सड़क परिवहन और राजमार्ग मंत्रालय ने बैटरी पैक आधार नंबर यानी BPAN फ्रेमवर्क का एक ड्राफ्ट प्रपोज किया है. इसका मकसद हर इलेक्ट्रिक व्हीकल की बैटरी को एक यूनिक आइडेंटिटी देना और उसके पूरे लाइफ साइकिल को आम लोगों के लिए ज्यादा बेहतर और पारदर्शी बनाना है. इस पहल से न सिर्फ आम कार मालिकों को फायदा मिलेगा, बल्कि इंडस्ट्री और सरकार दोनों के लिए निगरानी और सेफ्टी आसान होगी. तो आइये जानें क्या है ये नया BPAN मसौदा.
क्या है बैटरी पैक आधार नंबर BPAN BPAN
एक खास 21 अंकों का अल्फान्यूमेरिक आइडेंटिफिकेशन (पहचान) नंबर होगा, जो हर इलेक्ट्रिक व्हीकल की बैटरी को दिया जाएगा. यह नंबर QR कोड के रूप में भी मौजूद रहेगा, जिसे मशीन आसानी से पढ़ सकेगी. इसकी मदद से यह पता लगाया जा सकेगा कि बैटरी कब बनी, कहां लगी, कब सर्विस हुई और आखिर में उसका रिसाइक्लिंग कैसे हुआ. यह व्यवस्था पहले सुझाए गए बैटरी पासपोर्ट सिस्टम जैसी ही है, जिसे भारत और अन्य देशों में लागू करने पर विचार हो चुका है.
किन बैटरियों पर लागू होगा नियम
इस फ्रेमवर्क की शुरुआत इलेक्ट्रिक वाहनों की बैटरियों से होगी. आगे चलकर यह 2 kWh या उससे अधिक क्षमता वाली सभी बैटरियों पर लागू किया जा सकता है. हालांकि आम इलेक्ट्रॉनिक सामान में इस्तेमाल होने वाली छोटी बैटरियां इस नियम के दायरे में नहीं आएंगी. फिलहाल ये केवल इलेक्ट्रिक वाहनों वाले बैटरियों पर लागू किया जाएगा.
आपको क्या होगा फायदा
BPAN सिस्टम के जरिए ग्राहक अपनी बैटरी की मैन्युफैक्चरिंग तारीख, असली या नकली होने की जानकारी और बैटरी हेल्थ पर नज़र रख सकेंगे. इससे अनधिकृत बैटरी बदलने या छेड़छाड़ को रोका जा सकेगा. साथ ही बैटरी की लाइफ और उसकी क्वालिटी को लेकर भरोसा बढ़ेगा.
क्यों जरूरी है ये सिस्टम
सरकार और बैटरी निर्माताओं के लिए यह सिस्टम कच्चे माल की सोर्सिंग, ट्रांसपोर्ट, सेकंड लाइफ रियूज, सेफ रिसाइक्लिंग और मिनरल रिकवरी तक हर कदम पर पारदर्शिता लाएगा. बड़े स्तर पर डेटा मिलने से भविष्य में ज्यादा सुरक्षित, टिकाऊ और बेहतर बैटरियां बनाने में मदद मिलेगी. इसमें बीमा कंपनियां, पुरानी गाड़ी खरीदने वाले, बैंक, वेस्ट मैनेजमेंट एजेंसियां और सर्विस प्रोवाइडर को भी लाभ मिलेगा.
कौन सा डेटा होगा ट्रैक
BPAN के तहत बैटरी से जुड़ा कई तरह का डेटा स्टोर किया जाएगा. इसमें बैटरी मैन्युफैक्चरर आइडेंटिफायर, बैटरी डिस्क्रिप्टर, बैटरी आइडेंटिफायर, मटेरियल कंपोजिशन, कार्बन फुटप्रिंट और डायनामिक डेटा शामिल होगा. यह डेटा यूरोप में बन रहे बैटरी पासपोर्ट स्टैंडर्ड के जैसा ही होने की संभावना है. ताकि भविष्य में ग्लोबल स्टैंडर्ड से तालमेल बैठाया जा सके. सरकार इसके लिए एक ऑनलाइन पोर्टल भी बनाएगी.

BPAN में इलेक्ट्रिक कार की बैटरी से जुड़ी तमाम जानकारियां दर्ज होंगी. Photo: Screengrab
बैटरी पैक आधार में कैसी जानकारी होगी दर्ज
बैटरी पैक आधार सिस्टम को इस तरह तैयार किया गया है कि हर बैटरी की पूरी ट्रेसिंग संभव हो सके और बैटरी सेक्टर में सर्कुलर इकॉनमी को बढ़ावा मिले. खासतौर पर इलेक्ट्रिक वाहनों के लिए यह सिस्टम बेहद अहम माना जा रहा है. बैटरी पैक आधार के तहत हर बैटरी से जुड़ी कई जरूरी जानकारियां डिजिटल रूप से दर्ज की जाएंगी, जिससे उसकी पहचान, उपयोग और भविष्य की स्थिति को आसानी से समझा जा सकेगा. इसके मुख्य रूप से 6 हिस्से होंगे-
- बैटरी मैन्युफैक्चरर आइडेंटिफायर (BMI)
- बैटरी डिस्क्रिप्टर सेक्शन (BDS)
- बैटरी आइडेंटिफायर (BI)
- बैटरी मटेरियल कंपोजिशन सेक्शन (BMCS)
- बैटरी कार्बन फुटप्रिंट (BCF)
- बैटरी डायनामिक डेटा (BDD)
इस सिस्टम में सबसे पहले बैटरी मैन्युफैक्चरर आइडेंटिफायर यानी BMI शामिल होगा, जिससे यह साफ होगा कि बैटरी किस कंपनी ने बनाई है. इसके अलावा बैटरी डिस्क्रिप्टर सेक्शन यानी BDS में बैटरी का प्रकार, क्षमता और तकनीकी डिटेल दर्ज रहेगा. बैटरी आइडेंटिफायर यानी BI हर यूनिट को दी गई यूनिक पहचान होगी, जिससे किसी भी बैटरी को अलग से पहचाना जा सकेगा.
बैटरी मटेरियल कंपोजिशन सेक्शन यानी BMCS के जरिए यह जानकारी मिलेगी कि बैटरी में किन-किन कंपोनेंट्स और खनिजों का इस्तेमाल हुआ है. वहीं बैटरी कार्बन फुटप्रिंट यानी BCF से यह पता चलेगा कि बैटरी के निर्माण और उपयोग के दौरान पर्यावरण पर कितना असर पड़ा है. इसके साथ ही बैटरी डायनामिक डेटा यानी BDD में बैटरी की मौजूदा हेल्थ, चार्ज साइकल और परफॉर्मेंस से जुड़ा रियल टाइम डेटा शामिल होगा.
कब तक होगा लागू
इस सिस्टम को पूरी तरह लागू होने में अभी समय लग सकता है. इसमें कई महीने या साल भी लग सकते हैं. पहले भी ब्लॉकचेन, RFID और NFC जैसी तकनीकी पर बेस्ड प्रस्ताव सामने आ चुके हैं. सड़क परिवहन मंत्रालय ने इसके लिए एक विशेष समिति बनाई है, जिसमें IIT, ARAI, नीति आयोग और अन्य संस्थानों के एक्सपर्ट शामिल हैं. यह समिति इंडियन कंडिशन के हिसाब से नियम और लागू करने की रणनीति तय करेगी.
—- समाप्त —-
EV fire incident: NHEV issues safety recommendations to NITI Aayog
PUBLISHED: June 27, 2022, SOURCE: India Today
After the fire incident was reported in an electric SUV in Maharashtra, National Highway for Electric Vehicles has issued safety recommendations to NITI Aayog for EVs.

Days after a fire broke out in an electric vehicle (EV) of a leading Indian automobile company, the National Highway for Electric Vehicles (NHEV) has issued recommendations to the NITI Aayog over upkeep of EVs and its batteries.
The incident of fire in a compact electric SUV that was reported in Maharashtra created ripples in the rapidly going EV industry. While the government has already ordered a probe into the incident, the NHEV, in association with a private firm, has issued safety recommendations for EVs to avert repetition of such incidents.
We have divided the safety recommendations in three parts—administrative, technical and regulatory—for EVs. Under the administrative recommendations, real time identification of batteries and their current ownership details shall be available with the regulator and for this a unique identification of batteries is required so that digital ownership should be easily available.
Abhijeet Sinha, Project Director, NHEV
“Users deserve to know what they are buying, driving and risks associated, and there should be higher transparency to EV batteries and their components information and third-party coverage. Identifying the battery failures, volatile thermal behaviour and associated risk shall be explored and battery monitoring systems shall have a black box feature to capture the root cause of failure or fire to minimise post-incident investigations,” said Sinha.
Apart from issuing recommendations, the Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) has invited pilot applications for fire-resistant and safer batteries for EVs for a safer sail of the NHEV project.
— ENDS —
NHEV Working Group suggests identification of battery failure issues, a device to monitor fire incidents
PUBLISHED: June 27, 2022 | SOURCE: Business Line
The Charge Point operator’s (CPO) society will install 4,000-5,000 EV chargers at 2,000 locations in the central Delhi district.
The National Highways for Electric Vehicles (NHEV) on Monday made 12 safety recommendations related to battery swapping and charging infrastructure. The suggestions include identifying battery failure issues as well as monitor problems regarding battery fires through an identification device.
The NHEV organised a meeting of its working group and board members to brainstorm on issues related to ease of doing business and battery safety as well as swapping in electric vehicles (EVs) in India.
The deliberations were attended by National Project Director NHEV Abhijeet Sinha, Niti Aayog Member and Honorary Chair NHEV Knowledge Group V K Saraswat and NHEV Knowledge group & World Economic Forum Member Akhilesh Srivastava. Many key stakeholders from the EV industry also participated in the event, NHEV said in a statement.
“Today NHEV Working Group decided to place these 12 recommendations before the policy think tank and government along with four new short-term pilots announced. Charge Point Operator’s Society today passed the proposal in Its Board Meeting to make central Delhi a model district to address four bottlenecks which shall further be made available to all CPOs of India “ Sinha said.
Recommendations
The Working Group came up with 12 recommendations. Out of these 12 suggestions, four each are related with administrative, regulatory and technical recommendations.
“Four recommendations regarding regulatory aspects were also made. These are identification of battery failure issues, volatile thermal behavior and associated risks with an identification device to understand the root cause of failure, real-time verifiable exchange value for battery swapping, net metering of charging stations from Discoms, and financing (by bank and NBFCs) of only those batteries that meet government standardisation,” it said.
Other suggestions include real-time identification of batteries and their current ownership details with Unique Identification (UID), transparency in information exchange to customers regarding EV batteries, components and third-party damage coverage, user discretion regarding sharing their location & privacy, as well as ascertaining the financial stability of battery OEM to ensure the after-sales service and assistance during the battery’s life.
The technical suggestions include the provision of a black-box-like feature to monitor battery systems and identifying the issues that lead to battery failure, mandatory digital connectivity of the battery through e-sim or other means, monitoring the battery performance & recall in case of fault identification, and high-accelerated lifetime testing (HALT) for critical battery performance and operating parameters, NHEV said.
EV charging points in Central Delhi
During the event, another meeting was held by the Charge Point operator’s (CPO) society. After the meeting, it was announced that 4,000-5,000 EV chargers will be installed at 2,000 locations in the central Delhi district.
The idea is to develop central Delhi as India’s model district for Ease of Doing Business by making E-Mobility infrastructure easily accessible thus facilitating smooth business. The CPO society recommended this to remove the bottlenecks in the E-Mobility sector. The charging points will be installed by Joulepoint at locations like apartment buildings, malls, RWAs and hotels.
— ENDS —
NHEV safety recommendation
PUBLISHED: 27 June, 2022 | SOURCE: ElectricVehicles.in
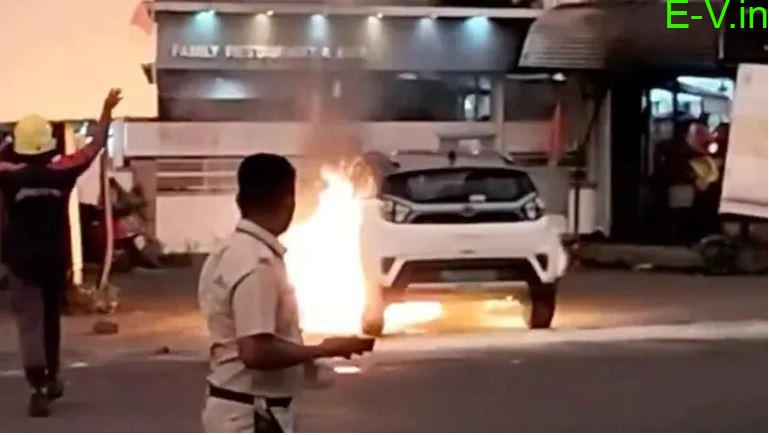

The National Highway for Electric vehicles (NHEV safety recommendation) has recently modified and added a few safety recommendations related to battery swapping and charging Electric vehicles infrastructure.
Suggestions include identifying battery failure as well as monitoring problems regarding battery fires through identification devices.
NHEV safety recommendation to know about what they are buying, driving, and risk associated, and there should be higher transparency to EV batteries and their components information and third-party coverage. Identifying the battery failures, volatile thermal behaviour, and associated risk shall be explored in battery monitoring systems.
The NHEV meeting was attended by a Niti Aayog Member and Honorary Chair of NHEV Knowledge Group, V.K Saraswat, and key stakeholders from the EV industry.
NHEV working Group decided to place these 12 recommendations before the policy think tank and government along with four new short-term pilots announced, said Abhijeet Sinha, National Project Director, NHEV.
In another meeting, the charging point operator’s (CPO) society also announced that 4,000 to 5,000 EV chargers will be installed at 2,000 locations in the central Delhi district.
The recommendations come as the government has ordered a probe into the Tata Motors Nexon EV fire incident in Mumbai.
The company termed it an isolated thermal incident. The Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), which was earlier tasked with investigating electric two-wheeler fire incidents by the Union Road transport,
and Highways Ministry, is leading the probe into the Nexon EV fire. The DRDO probe had earlier found serious defects in the EV two-wheeler batteries.
These defects occurred because the electric two-wheeler manufacturers like Okinawa Autotech, Pure EV, Jitendra Electric Vehicles, Ola Electric, and Boom Motors may have used “lower-grade materials to cut costs”.
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has issued new performance standards for Lithium-ion batteries to safeguard the consumers amid the rising EV fire episodes in the country.
— ENDS —